Story By: Kathryn Quinn, Sub Editor: Joseph Golder, Agency: CEN
These deadly ticks which carry an Ebola-like virus are apparently spreading across Europe amid claims they have mutated after being found in the UK.
So far this year, six Hyalomma ticks have been found in Germany and experts believe they have mutated to survive the cold winters.
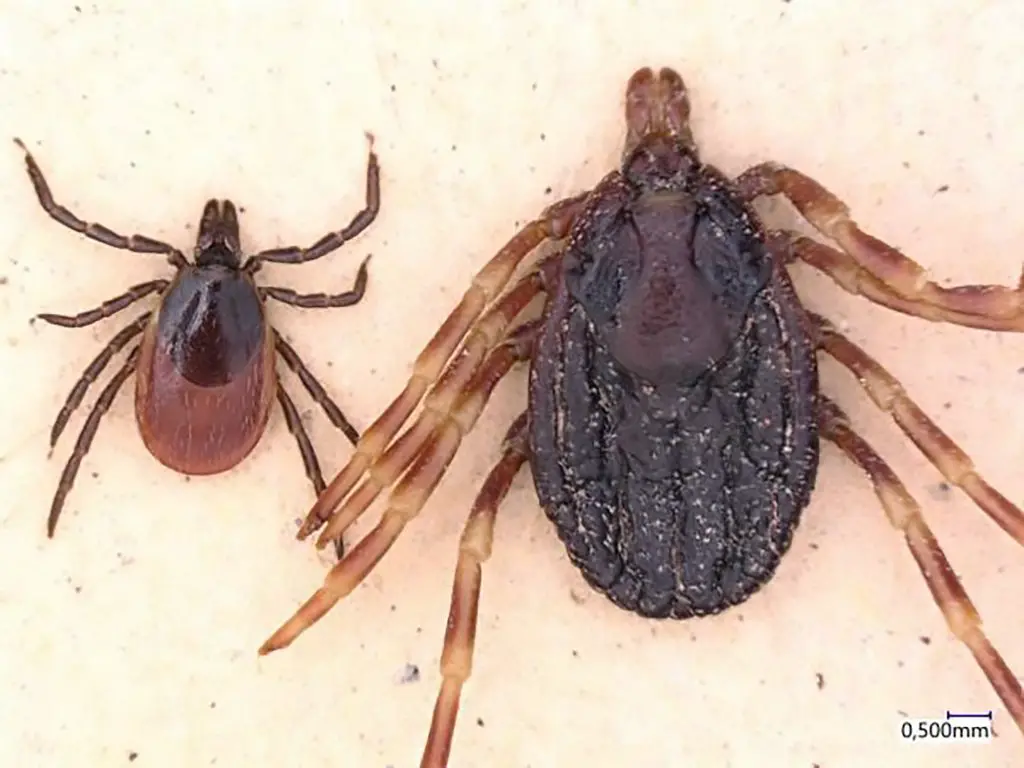

Experts at the University of Hohenheim and the Institute for Microbiology of the German Federal Armed Forces in Munich have confirmed six new specimens have been found.
Hohenheim parasitologist and tick expert Ute Mackenstedt said: “According to the latest evidence, we have to presume that these animals are able to survive the winters in Germany.
Only last year experts had warned about the rising number of Hyalomma ticks being found in Germany, thought to be because of rising temperatures.
The Hyalomma ticks are very noticeable and can grow to as long as two centimetres (0.8 inches), substantially larger than the local common wood tick (Ixodes ricinus). They are recognised by their unusual size and their striped legs.
Until now, Hyalomma ticks were thought to have been brought to Germany by migratory birds. However, Mackenstedt believes that this cannot have been the case this year, saying: “If the development cycle is taken into account, this cannot be the case here, as the ticks would have had to have been introduced at a time where the migratory birds had not even arrived.”
But the expert also pointed out that this does not mean that the Hyalomma are home grown. “For the population to expand, a male and a female tick would have to find each other. This is very difficult with such a small number.
However, five of the Hyalomma ticks were found on a horse at a stables meaning there is the possibility of a possible pairing and as a result the emergence of an independent population.
Last year German scientists warned about several tropical ticks living in the country. Scientists registered a total of seven specimens of the genus Hyalomma in Lower Saxony and Hesse in August 2018, the University of Hohenheim and the Institute for Microbiology of the German Federal Armed Forces in Munich confirmed, meanwhile only two tropical ticks have been found in Germany before, one in 2015 and one in 2017.
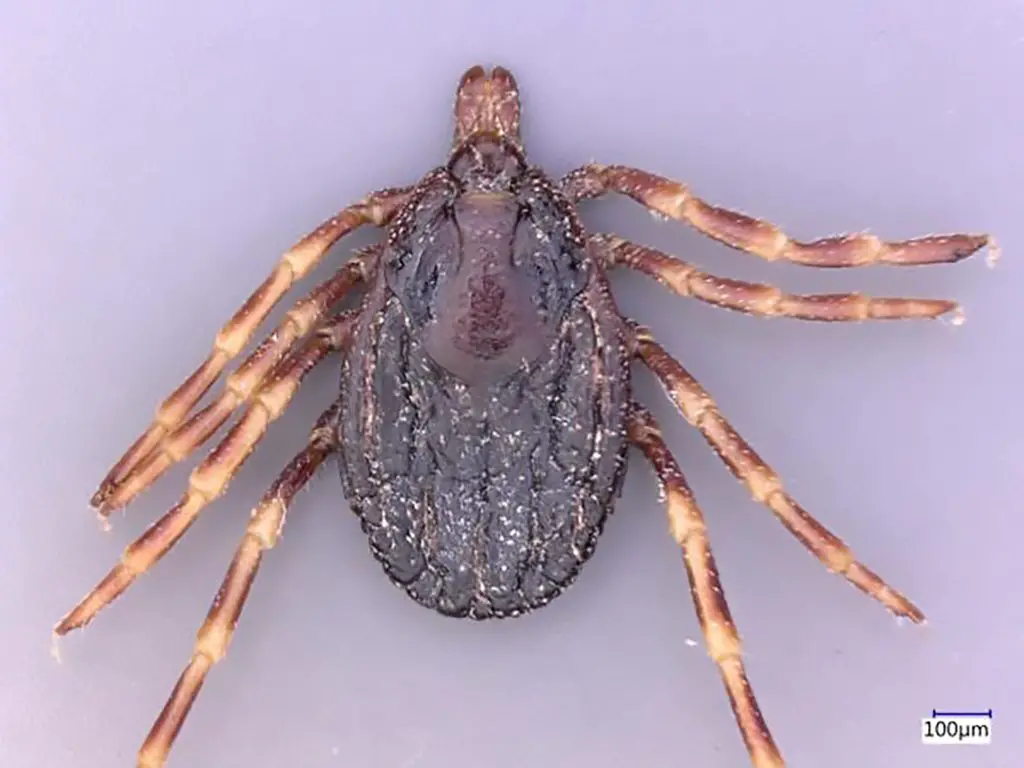

A tick carrying the illness, which is categorised as a hemorrhagic fever virus, was discovered by medics in Dorset in 2018, according to Public Health England, although it is unclear if there have been any reported cases in Britain so far this year.
Ebola is also categorised as a hemorrhagic fever virus according to the World Health Organisation.
Switzerland has also reported finding Hyalomma ticks. Swiss experts had also to date believed that the ticks were brought by migratory birds.
Hyalomma is a genus of hard-bodied ticks common in Asia, Europe, and North Africa. They are also found in Southern Africa. Hyalomma originated from Iran or the southern part of the former Soviet Union and spread into Asia, the Middle East, southern Europe, and Africa. Adult Hyalomma can bite humans and transmit serious pathogens.
Tick bites can cause a number of diseases which in some cases can be fatal such tick-borne encephalitis and Lyme disease. Hyalomma species can also carry Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever, which has not yet occurred in Germany. Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever can cause death in up to thirty percent of people who catch the disease.
The researchers fear that the ticks may become a permanent feature in Germany as temperatures rise. Their presence was put down to the hot, dry summer in Germany, as they prefer a lower humidity than the ticks usually found in this country.
The ViralTab page is created by and dedicated to professional, independent freelance journalists. It is a place for us to showcase our work. When our news is sold to our media partners, we will include the link here.