Boffins in Germany have discovered a previously unknown genus of dinosaur that roamed Europe 200 million years ago.
Researchers from the University of Tuebingen reanalysed a dinosaur skeleton found in Trossingen, south-western Germany, in 1992.
They found that many of the bones did not correspond to those of a typical plateosaur, as previously thought.
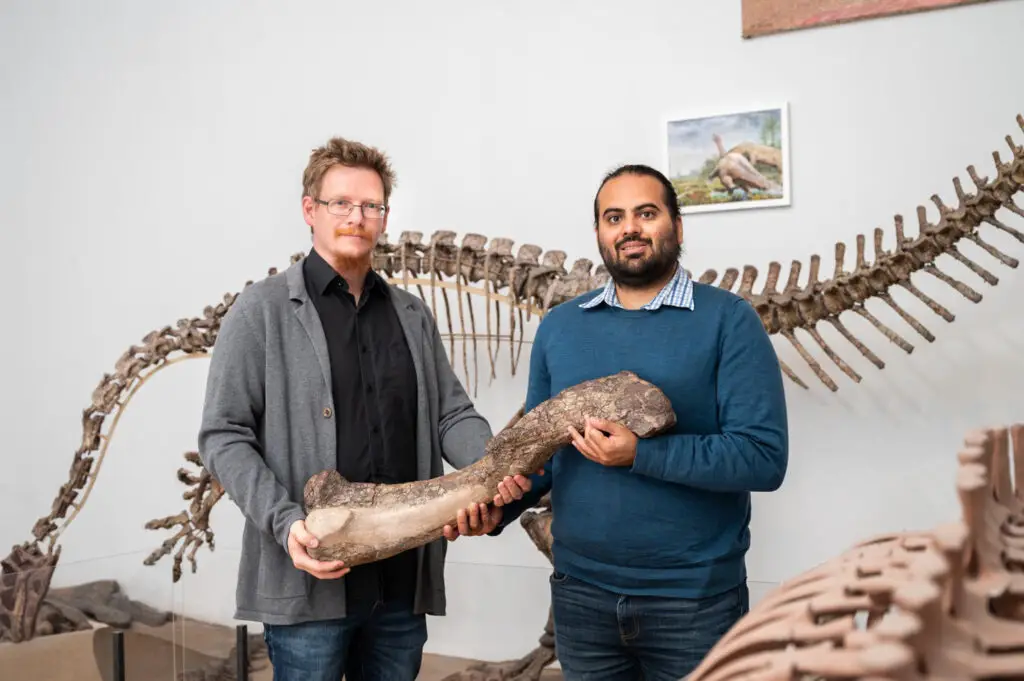

They quickly realised they were dealing with not only a new species but a whole new genus, which they named Tuebingosaurussank, in tribute to their university town.
The species – Tuebingosaurus maierfritzorum – lived in what is now the Swabian Jura mountain range approximately 203 to 211 million years ago.
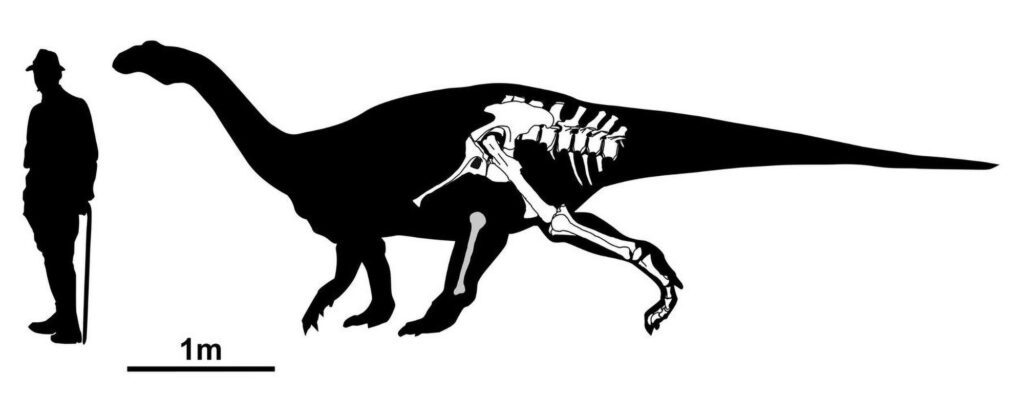
It was a herbivore and most likely a quadruped.
In a statement obtained by Newsflash on 8th September, the University of Tuebingen said: “Paleontologists at the University of Tuebingen’s Senckenberg Centre for Human Evolution and Palaeoenvironment have discovered a hitherto unknown genus and species of dinosaur. Tuebingosaurus maierfritzorum lived about 203 to 211 million years ago in the region now known as Swabian Alb and was a herbivore. The new species displays similarities with the large long-necked dinosaurs known as sauropods, and was identified when already-known dinosaur bones were re-examined. The results have been published in Vertebrate Zoology.
“The fossils, which are part of Tuebingen’s paleontological collection, were previously interpreted as Plateosauridae remains. Now, in a large-scale project, scientists Dr. Omar Rafael Regalado Fernandez and PD Dr. Ingmar Werneburg have re-examined all the dinosaur bones stored in Tuebingen. Most of the fossils originate from a quarry near Trossingen at the edge of Swabian Alb, where many dinosaur bones found since the 19th century have frequently been classified as Plateosaurus.
“While it is undisputed that this group of dinosaurs was very common in parts of Europe about 200 million years ago, contemporary paleontologists are well aware that taxonomical classification in the past was often inaccurate, with some discoveries being too rapidly attributed to the Plateosaurus genus.
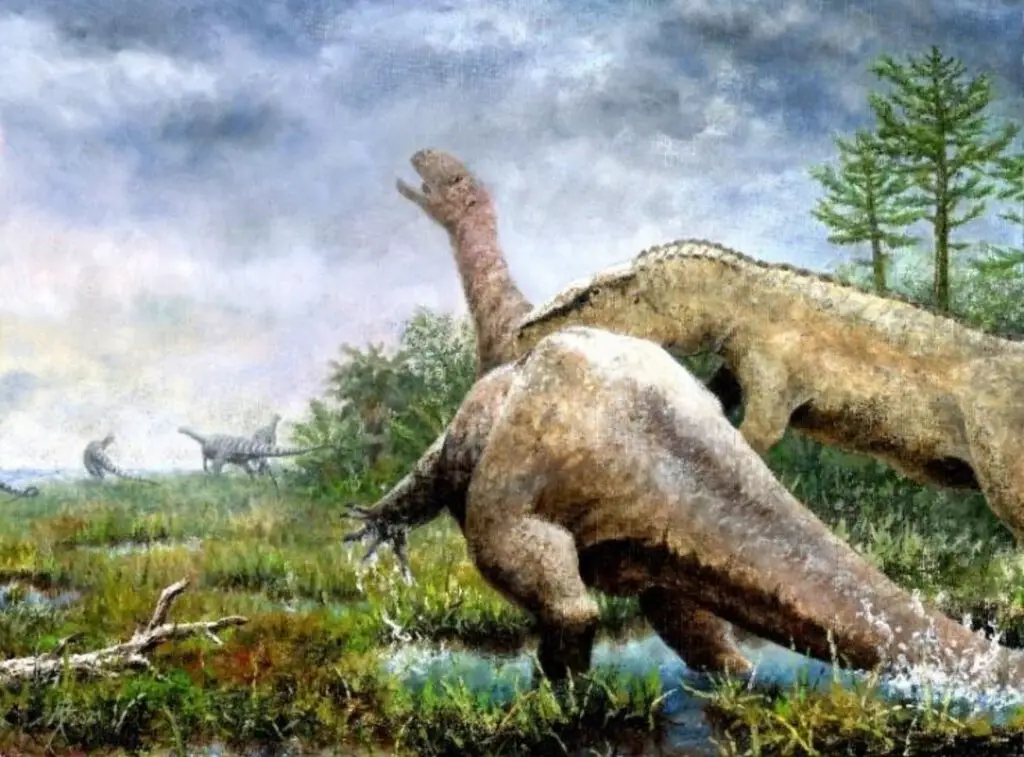

“When they re-analyzed a skeleton that was discovered in Trossingen in 1922, consisting mainly of the rear of the body, Regalado Fernandez and Werneburg established that many of the bones were not the same as a typical Plateosaurus. For instance, the partial skeleton displayed, among other derived characters, broader and more strongly-built hips with fused sacral vertebrae as well as unusually large and robust long bones – both features implied locomotion on four legs. This is unlike the Plateosauridae, which although resembling the long-necked sauropods from the Jura region likely moved on only two legs.
“Following in-depth comparison of all anatomical characteristics, the scientists recategorized the partial skeleton from Trossingen in the dinosaur tree of life and established that they had discovered a previously unknown species and genus. It is highly probable that Tuebingosaurus maierfritzorum was a quadruped and accordingly far more closely related to the later large sauropods such as Brachiosaurus or Diplodocus than with the Plateosauridae. The surrounding sedimentary rock and the preservation of the bones indicate that this Tuebingosaurus had sunk into a swamp and died. The bones on the left side of the body were probably on the surface and exposed to the elements for several years.”
Werneburg said: “Its genus name, Tuebingosaurus, is a homage to our beautiful university city and its inhabitants.”

The statement continued: “The species name maierfritzorum is a tribute to the two German zoologists, Professor Wolfgang Maier from Tuebingen and Professor Uwe Fritz from Senckenberg Natural History Collections Dresden. The new species has now been described in the latest edition of the Senckenberg Natural Science Society’s journal Vertebrate Zoology, which also pays tribute to Wolfgang Maier on his 80th birthday.
“In sum, the scientists have been able to show by their project that the early European dinosaurs were far more diverse than previously thought. The individual parts of the skeleton of Tuebingosaurus maierfritzorum, which until now have been stored separately, are now reunited and can be seen in two large display cabinets. Besides thousands of other treasures, there are two complete Plateosaurus skeletons from Trossingen, partial skeletons of two sauropods and one stegosaur from Tanzania to wonder at in Tuebingen’s paleontological collection.”



